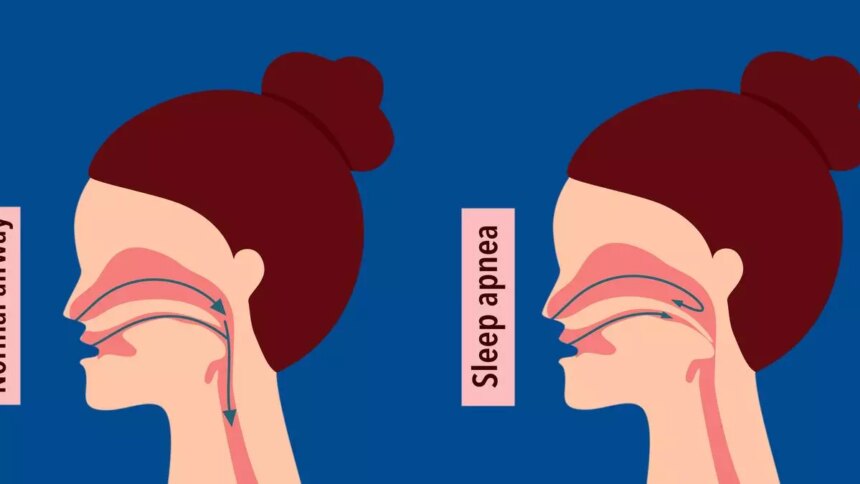
The recent FDA approval of Zepbound (tirzepatide) for the treatment of moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) in adults with obesity marks a significant milestone in the management of this common condition. OSA occurs when the upper airway becomes blocked during sleep, leading to pauses in breathing. This condition is more prevalent in individuals with obesity, making the approval of Zepbound particularly relevant for this population.
Zepbound works by activating receptors of hormones secreted from the intestine to reduce appetite and food intake, ultimately leading to weight loss. Studies have shown that by reducing body weight, Zepbound can also improve symptoms of OSA. The approval of Zepbound for moderate to severe OSA in adults with obesity was based on two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies involving 469 adults without type 2 diabetes. Participants treated with Zepbound showed a significant decrease in body weight compared to those who received a placebo.
While Zepbound offers a new treatment option for individuals with OSA, it is important to be aware of the potential side effects associated with the medication. These side effects include nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain, injection site reactions, hypersensitivity or allergic reactions, and the possibility of thyroid C-cell tumors. Zepbound also carries warnings for pancreatitis, hypoglycemia, suicidal behavior, and other risks.
The approval of Zepbound by the FDA represents a significant advancement in the management of OSA in adults with obesity. By addressing both weight management and OSA symptoms, Zepbound provides a comprehensive approach to improving the health and quality of life of individuals affected by this condition. It is recommended that individuals discuss the potential benefits and risks of Zepbound with their healthcare provider to determine if it is an appropriate treatment option for them.