Understanding the Wildfires Ravaging Los Angeles: Current Events and Climate Factors
Overview of the Situation
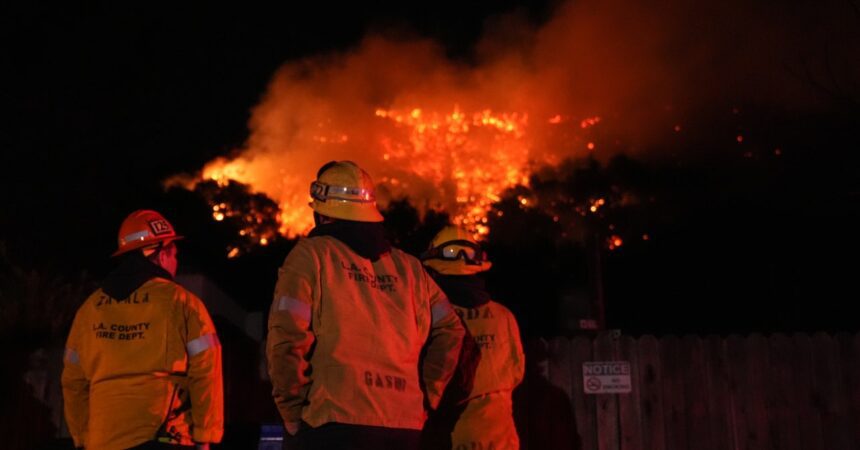
As of late January 2024, wildfires are wreaking havoc across the Los Angeles metro area, contributing to mandatory evacuations and widespread school closures. With five major blazes raging throughout the region, firefighting efforts are challenged by a cocktail of meteorological conditions that raises the stakes for both current and future fire events. The Palisades Fire and Eaton Fire have particularly drawn attention, consuming tens of thousands of acres and leading to the destruction of thousands of structures as well as a tragic loss of life.
The Fire Crisis in Los Angeles
The impacts of the wildfires are far-reaching, affecting communities, wildlife, and air quality across California. The Palisades Fire has scorched over 20,000 acres, while the Eaton Fire has grown to exceed 10,000 acres. Reports estimate at least 10,000 structures have been destroyed, and tragically, 10 fatalities have been confirmed. The rapid spread of these fires has been attributed to:
- Vegetation: The underbrush is exceptionally dry due to prolonged periods with little to no rainfall, creating highly flammable conditions.
- Low Humidity: Humidity levels remain critically low, further exacerbating the potential for wildfires.
- Strong Winds: Stiff winds, driven by the Santa Ana conditions, have propelled the flames and made firefighting efforts more complicated.
The Meteorological Conditions at Play
The Santa Ana Winds
Understanding the Santa Ana winds is crucial to comprehending the wildfire dynamics in Southern California. These winds occur when a pressure difference between the Great Basin and coastal areas, notably Los Angeles, results in strong gusts heading toward the coast. The stronger the pressure differential, the more intense the wind, which can rapidly spread existing fires.
Meteorologists are predicting two moderate Santa Ana wind events in the upcoming days—one on Sunday and potentially another on Tuesday. These winds pose a two-fold threat: they not only promote the spread of wildfires but also make ignition of new blazes more likely.
Impact of La Niña
Compounding the wildfire challenges is the current La Niña phenomenon. This climate pattern leads to colder-than-normal sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean, which can disrupt typical storm tracks. As a result, the Gulf of Alaska remains the primary destination for storms, with very little rain reaching the dry Southern California landscape.
Despite being in the middle of Southern California’s rainy season, Los Angeles International Airport recorded only 0.03 inches of rain since the start of last summer. The absence of rain amid a season that usually brings moisture only serves to deepen the drought-like conditions destabilizing the region’s vegetation.
Implications and Future Outlook
Forecasters indicate that the ongoing weak La Niña pattern could persist through the remainder of winter, possibly fading by spring, coinciding with the onset of Southern California’s dry season. This scenario presents a grim outlook for fire-prone areas, as dry conditions will continue to foster fire-weather risks.
While there may be potential for some precipitation as we progress into spring, significant chances of rain over the next week and a half appear slim. The ongoing conditions suggest a sustained need for vigilance in fire prevention and resource allocation for firefighting.
Conclusion
The wildfires currently impacting Los Angeles emphasize the urgent need for a multifaceted approach to disaster management that includes climate adaptation strategies. Continuous monitoring of weather patterns, proactive vegetation management, and investments in firefighting resources are essential to mitigate the risks associated with future wildfires. As climate change continues to exacerbate drought conditions and alter weather patterns, communities must prioritize preparedness, resilience, and recovery strategies to protect both lives and property in the face of ongoing climatic challenges.
As we continue to monitor the situation, it’s imperative for residents to stay informed about evacuation orders and fire advisories while advocating for longer-term solutions to the complex relationship between climate and wildfire behavior.